In the dynamic world of Forex trading, where currencies fluctuate with global events and economic indicators, having a tool that can sift through the noise and identify real market sentiment is invaluable. The Chaikin Money Flow (CMF) stands out as such a tool, offering traders a nuanced understanding of buying and selling pressures that govern currency movements. This comprehensive guide dives deep into the CMF, illustrating its mechanics, application, and strategic importance in Forex trading.
Understanding the Foundations of Chaikin Money Flow
The CMF, developed by Marc Chaikin, is a volume-weighted average of accumulation and distribution over a specified period. Unlike simple price indicators, the CMF incorporates volume to give a fuller picture of market sentiment, making it a critical indicator for Forex traders.
The Formula Behind Chaikin Money Flow
The essence of the CMF lies in its formula, which integrates price movement and volume:
- Money Flow Multiplier:
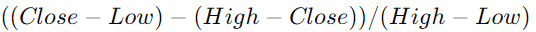
- Money Flow Volume: Money Flow Multiplier × Volume for the period
- CMF:
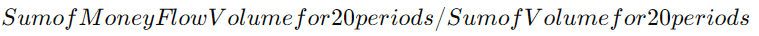
This calculation reveals not just where the price closed within its range but how much volume supported the move, offering insights into market conviction behind price movements.
Decoding the Signals: A Deep Dive into CMF Interpretation
A positive CMF value indicates that the market is under accumulation, suggesting buying pressure, while a negative CMF value signifies distribution or selling pressure. It’s the subtleties within these broad strokes where the CMF truly shines, allowing traders to discern the strength of trends and potential reversals with greater accuracy.
Strategic Application of Chaikin Money Flow in Forex Trading
Incorporating the CMF into a Forex trading strategy can significantly enhance decision-making processes, providing clarity on when to enter or exit trades based on underlying market sentiment and liquidity.
Harnessing CMF for Entry and Exit Points
- Entry Signals: A crossing of the CMF above zero can be a robust entry signal, indicating that buying pressure is starting to outweigh selling pressure. For example, if the EUR/USD pair shows a rising CMF crossing above zero, it suggests an opportune moment to consider going long on the pair.
- Exit Signals: Conversely, a CMF crossing below zero suggests growing selling pressure and might serve as a signal to exit a position or even consider short selling.
Combining CMF with Other Technical Indicators
No indicator should be used in isolation, and the CMF is no exception. Combining it with trend indicators like Moving Averages or momentum indicators like the Relative Strength Index (RSI) can provide a comprehensive view of the market. For instance, a trader might look for scenarios where the CMF is positive and the currency pair is trading above its 50-day Moving Average, reinforcing the decision to stay in a long position.
Analyzing Market Conditions with Chaikin Money Flow
The true value of the CMF comes from its ability to provide a window into the market’s soul, revealing not just the direction of market sentiment but its intensity.
Interpreting High and Low CMF Values
- Sustained Positive Values: A CMF that remains positive over an extended period suggests strong buying interest, often preceding upward price movements. For currencies, this could indicate sustained investor confidence in a country’s economic outlook or interest rate trajectory.
- Persistently Negative Values: Similarly, a CMF that stays negative over time signals continued selling pressure, which could be due to negative economic forecasts or geopolitical uncertainties affecting currency value.
The Significance of Zero Line Crosses
The point at which the CMF crosses the zero line is a moment of equilibrium between buying and selling pressures, often signaling a potential change in market sentiment. A strategic trader will monitor these crosses closely, using them as precursors to shifts in market direction.
Practical Insights: Chaikin Money Flow in Action
To solidify understanding, let’s explore a hypothetical scenario in the Forex market involving the British Pound (GBP/USD).
Case Study: GBP/USD and the Chaikin Money Flow
Imagine the GBP/USD has been in a downtrend, but you notice the CMF starting to climb, moving from negative to positive territory. This shift suggests that buying pressure is increasing, potentially indicating a reversal or significant pullback in the downtrend. As the CMF crosses above zero, it might be an optimal time to enter a long position, anticipating a rise in the GBP/USD pair.
The key here is confirmation. If the positive CMF is accompanied by other bullish signals, such as an upward crossover in MACD or the price moving above a significant moving average, the case for entering a long position strengthens.

Common Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
While the CMF is a powerful tool, it’s not foolproof. Here are common pitfalls and how to sidestep them:
- Overreliance on Short-term Fluctuations: The CMF can be volatile in the short term. Traders should focus on longer-term CMF trends and corroborate with other indicators to make informed decisions.
- Ignoring Market Context: Always consider the broader market context. A positive CMF in a strong downtrend might not signal a reversal but a temporary pause.
Conclusion: Mastering Market Sentiment with Chaikin Money Flow
The Chaikin Money Flow is more than just an indicator; it’s a lens through which the ebb and flow of market sentiment can be viewed with clarity and precision. By mastering its use, Forex traders can navigate the market with an informed perspective, making decisions not just based on price movements, but on the underlying buying and selling pressures that drive those movements. Like any tool, success with the CMF comes down to practice, patience, and integration into a well-rounded trading strategy.

FAQs About Chaikin Money Flow
What is Chaikin Money Flow?
Chaikin Money Flow (CMF) is a technical analysis indicator used to measure the volume-weighted average of accumulation and distribution over a set period. It combines price and volume to indicate buying or selling pressure, aiming to predict future market movements based on current sentiment.
How is Chaikin Money Flow calculated?
The CMF is calculated by first finding the Money Flow Multiplier, which highlights where the close is within the period’s range. The multiplier is then multiplied by the period’s volume to get the Money Flow Volume. The CMF is the sum of Money Flow Volume for the chosen period (usually 20 or 21 days) divided by the sum of volume for the same period.
What does a positive vs. negative CMF indicate?
A positive CMF value suggests that buying pressure is dominant, indicating accumulation. This can be a sign of bullish sentiment, potentially leading to an upward price movement. A negative CMF value, on the other hand, indicates selling pressure or distribution, suggesting bearish sentiment and possible downward price movement.
Can the Chaikin Money Flow be used for all trading instruments?
Yes, the CMF can be applied to various trading instruments, including stocks, forex, commodities, and indices. Its utility in showing market sentiment through volume and price action makes it versatile across different markets.
How can traders use CMF to make trading decisions?
Traders can use CMF to identify potential buy or sell signals through divergence with price action or when the CMF crosses above or below zero. For example, a divergence occurs when the price reaches new highs or lows without being accompanied by a corresponding new high or low in the CMF, potentially indicating a reversal.
What are the limitations of Chaikin Money Flow?
While CMF is a powerful tool for gauging market sentiment, it has limitations. It might not always predict market reversals accurately, especially in volatile markets. Also, relying solely on CMF without considering other factors like market trends or news events can lead to misinterpretation of signals.
How does CMF differ from other volume indicators?
CMF is unique because it incorporates both price and volume over a set period to determine market sentiment, unlike other volume indicators that may only consider volume. This combination allows for a more nuanced view of buying and selling pressure.
Can CMF be used in a trending market?
Yes, CMF can be particularly useful in trending markets to confirm the strength of the trend. In uptrends, a persistently positive CMF indicates strong buying pressure, while in downtrends, a persistently negative CMF indicates strong selling pressure.
What period setting is best for CMF?
The standard period setting for CMF is 20 or 21 days, which works well for many traders. However, traders may adjust this setting based on their trading style, with shorter periods for more sensitivity or longer periods for smoother data.
How should a trader act on divergences identified by CMF?
Divergences between CMF and price action can signal potential reversals. If price makes new highs while CMF fails to do so, it may indicate weakening momentum and a possible bearish reversal. Conversely, if price makes new lows but CMF does not, it could signal a bullish reversal. Traders should look for additional confirmation before acting on these signals.